Smart cities require new professional profiles
By 2050, 68% of the world’s population is projected to live in cities, according to UN data. This will generate a series of problems such as energy supply, service provision, urbanization, waste management and mobility, among others.
20 Apr 2020
Faced with this reality, cities have two challenges ahead: transforming into Smart Cities and finding qualified professionals to lead that transformation.
What are Smart Cities?
Smart Cities are the result of cooperation, innovation and development, both technological and economic, to develop more efficient, sustainable and comfortable cities. They are cities that apply technological solutions with the aim of effectively managing resources, promoting sustainable development, optimizing economic costs and responding to the demand for services from their citizens.
Technologies such as Big Data or the Internet of Things (IoT) are increasingly present in our environment and the concept of Smart City is no longer a term for the future, but for the present. In addition, adaptation and application projects for new technologies are being carried out both in large cities and in small municipalities, making Smart Cities become a reality that is spreading throughout the territory day by day.
Which sectors require new professional profiles?
New city models have already begun to generate new employment opportunities. Traditional professions are undergoing a complete renovation, and profiles that until now were the most requested are being relegated by others in which technology, collaborative work, innovation and the capacity for analysis and response are common characteristics.
The European Union in its report “Mapping Smart Cities in the EU” focuses the development of new cities, in six areas: Citizenship, Lifestyle and social cohesion, Governance, Environment, Mobility and Economy. These areas that will need new professional profiles are:
- The training of citizens in digital skills is key to the development of creativity and urban innovation. It is essential to work to reduce the digital divide in our society as much as possible, since day by day we see how many daily sectors are digitized, from banking to supermarkets, and efforts must be focused to make cities fully inclusive.
- EHealth applications are increasingly in demand. The apps about nutrition, sports or health are already on our mobile screens. And there is a breakthrough in content reporting for healthcare professionals. The ‘Cities for Global Health’ platform is a good example.
- Tourism and Leisure: There are great business opportunities in the exploitation of tourist services based on ICT applications, promoting ecological, sustainable, more attractive and personalized tourism for each person. Through technology, the accessibility and information of tourist destinations is improved and this favors the experience of visitors.
- Industry 4.0 is a concept that many experts define as “the fourth industrial revolution”. In the factories of the future, technologies such as Big Data, the Internet of Things, 3D printing, virtual and augmented reality or cloud computing will be fundamental. According to the report “Digitization creates or destroys jobs” by Randstad Research, by 2021, the digitization of processes is expected to have generated 1,250,000 jobs. Of these, 390,000 will be jobs in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (known as STEM).
- The e-commerce sector has experienced a spectacular increase in recent years worldwide. The demand for professionals specialized in e-commerce or digital marketing has increased very significantly to the detriment of traditional commercial sales. Online sales and digital communication represent a current and future challenge for small and medium-sized companies that are already adapting to it and investing so as not to be left behind.
- Data management and cybersecurity. Today it is already one of the most demanded professional profiles. The large amount of data that is handled through connected devices and sensors requires this type of professional who knows how to interpret it and anticipate future needs. And of course, that they guarantee security and transparency in the collection, processing and use of these data.
- One of the keys to Smart cities is the regulation of transport for its optimization and improvement of coexistence. Energy efficiency and more sustainable mobility will require managers to apply solutions and solve these challenges. These professionals will be trained to develop Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans, which promote habits such as mobility on foot, bicycle or use of public transport and the implementation of technologies for the collection of information and its control.
- Building and Energy. Solutions related to improving the energy efficiency of homes and their habitability are essential in the context of smart cities. The building is already moving towards more sustainable forms of construction such as passive houses, bioclimatic architecture or construction with sustainable and more durable and accessible materials. Building professionals have to direct their efforts to the integration of new technologies that result in smart cities, with a decrease in consumption in: lighting, energy, water … The analysis of all this data and the implementation of solutions will be essential for improving society.

These sectors are already introducing important changes in the skills and capacities that their candidates demand, so continuous training in transversal areas is a very important factor:
- Change is constant in cities and jobs closely linked to new technologies. Applications and technologies are constantly innovating and professionals capable of quickly adapting to new realities are needed.
- Leadership and planning skills for managing work teams and training new professionals in digital and remote environments.
- Creativity, especially in the search for solutions to new problems and challenges that will be presented in digitized environments and Smart cities.
- Essential teamwork in a society increasingly connected and made up of multidisciplinary, multi-ethnic and multitasking teams. Coordination, communication and planning are essential for everything to work properly.
- Analytical thinking. Local governance will be based on the analysis and interpretation of data reported by thousands of connected sensors, which, in turn, will report the opinions of citizens.
- Continuous learning ability. In a context of continuous change, the permanent recycling of our knowledge and skills is essential.
- Fluent in English and other languages. In an increasingly globalized world, languages are key to improving competitiveness within companies.
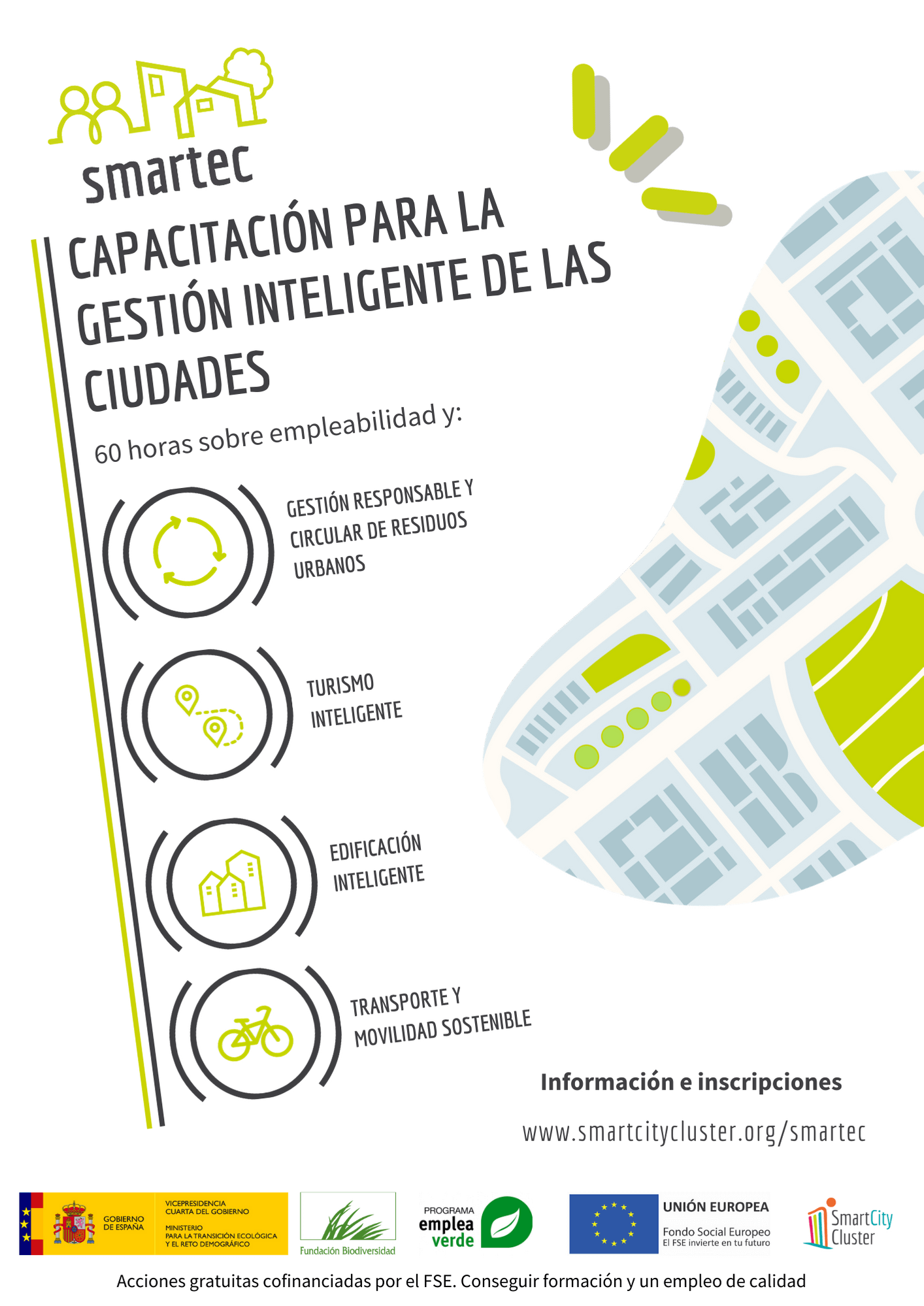
Smartec, training for new professionals in Smart cities
From Smart City Cluster, we are committed to training future professionals, so that they are the ones who lead the technological, social and environmental development that their cities require.
To do this, we have launched Smartec, a training project focused on four sectors: sustainable transport and mobility, smart building, responsible and circular management of urban waste, and smart tourism. It is a training program aimed at unemployed people in Andalusia and Extremadura, who want to learn about the new opportunities offered by new technologies in these 4 sectors, as well as improve their employability and job skills.
Smart Cities need professionals who create sustainable, smart and inclusive cities. You sign up?
+ Related post
Know the advantages of being associated
Smart City Cluster enhances collaboration among its partners, favoring research, development and innovation in the different solutions and technologies aimed at the development of smart cities.
Smart City Cluster is an alliance of private companies and institutions that work for the development of smart cities.